How Health Insurance Policies Work: Health insurance is an agreement in which an insurance company covers most medical, surgical, and preventive care expenses in exchange for regular monthly premiums. When you receive care, the insurer processes a claim to determine the covered services and payment share, while you pay the remaining out-of-pocket costs. Typically, higher premiums mean lower out-of-pocket expenses.
Health insurance can often feel like a complicated maze of paperwork, jargon, and endless fine print. But at its core, it’s one of the most important financial safety nets you can have in life. Medical emergencies don’t knock on the door before arriving, and healthcare costs are rising every single year.
Without proper coverage, even a single hospital stay can drain your savings. Understanding how health insurance policies work is the first step to protecting both your health and your wallet. Let’s break it down in detail so you can make smart, informed decisions about your health coverage.
Health Insurance

What is Health Insurance?
Health insurance is a financial agreement between you and an insurance company. Simply put, you pay a regular premium, and in return, the insurer covers a large portion of your medical expenses when you fall sick or get injured. Think of it as a safety shield that cushions you against high healthcare costs. Instead of paying hefty bills out of pocket, your insurance policy steps in to handle most of the expenses.
For example, if you need surgery costing $10,000, and your insurance covers 80% after your deductible, you only pay a fraction while your insurer covers the majority. Without insurance, that same surgery could wipe out your savings in an instant.
Importance of Health Insurance in Today’s World
Why is health insurance so important today? The answer is simple: healthcare is expensive. From diagnostic tests to medicines, doctor visits to emergency surgeries, costs have skyrocketed. A simple overnight hospital stay can run into thousands of dollars, and a critical illness like cancer or heart disease could financially cripple a family without insurance.
Moreover, health insurance isn’t just about money; it’s about access. Many top hospitals and doctors may only treat insured patients or those who can pay upfront. Having health insurance ensures you can receive quality medical care without worrying about cost at every step.
It’s also a legal or corporate necessity in many countries. For instance, in the U.S., the Affordable Care Act made health insurance a basic requirement. In the USA, health insurance is increasingly encouraged with government-backed plans. Wherever you are, one thing is clear: health insurance isn’t optional anymore, it’s essential.
Basics of Health Insurance Policies

How Health Insurance Works
At its heart, health insurance works like a partnership between you and your insurance company. You agree to pay premiums (monthly or yearly), and the insurer promises to cover certain medical expenses when the need arises. When you get sick or require treatment, you file a claim. If the expenses are covered under your policy, the insurer pays for them either directly to the hospital or by reimbursing you later.
The beauty of health insurance is in risk-sharing. By pooling together money from thousands of policyholders, insurers create a large fund. This fund is then used to pay for the medical costs of those who fall ill. It’s a system based on probabilities; some people may never need insurance in a given year, while others may need extensive treatment. This balance keeps the system sustainable.
Key Terms You Need to Know
Health insurance comes with its own dictionary of terms that can sound overwhelming. Here are the most important ones:
-
Premium: The fixed amount you pay regularly (monthly/annually) to keep your policy active.
-
Deductible: The initial out-of-pocket cost you must pay before your insurer starts covering expenses.
-
Copayment (Copay): A small fixed fee you pay for certain services, like $20 for a doctor’s visit.
-
Coinsurance: Your share of the medical cost, usually expressed as a percentage (e.g., you pay 20%, insurer pays 80%).
-
Exclusions: Conditions or treatments that your policy does not cover.
How Coverage is Determined
Not all health insurance policies are created equal. Coverage depends on the type of plan you choose and the insurer’s terms. Some plans may cover only hospitalization, while others extend to maternity, dental, or even mental health services. Coverage is also determined by factors like:
-
Age of the insured person
-
Pre-existing medical conditions
-
Chosen sum insured (coverage amount)
-
Waiting periods for specific illnesses
Types of Health Insurance Plans
![]()
Individual Health Insurance Plans
An individual health insurance policy is designed to cover just one person. The premium is calculated based on your age, health history, and lifestyle factors. These plans are ideal for singles, freelancers, or those who don’t get coverage from an employer.
The biggest advantage of individual plans is flexibility. You get to choose your sum insured, add-ons, and hospital network. However, if you have dependents, you might need to purchase separate policies for each family member, which can increase costs.
Family Health Insurance Plans
Family plans, also known as family floater policies, cover multiple family members under a single sum insured. For example, a $100,000 coverage amount can be shared between parents and children. The advantage here is affordability; covering everyone in one policy is usually cheaper than buying individual policies for each member.
However, the downside is that if one member requires extensive treatment, the entire coverage amount could be used up, leaving little or nothing for the others during the same year.
Group Health Insurance Policies
Group health insurance is typically offered by employers to their employees. Premiums are much lower since the risk is spread across a large group. Often, group policies also cover pre-existing conditions without waiting periods, making them a great benefit for employees.
The catch? Group health insurance ends when you leave the job. If you solely rely on employer-provided coverage and suddenly resign, you might find yourself without protection until you buy a personal plan.
Government-Sponsored Health Insurance Programs
The U.S. government also provides health insurance programs to expand access to healthcare. Medicare covers seniors and people with certain disabilities, while Medicaid helps low-income individuals and families. These programs are funded and subsidized by the federal and state governments, making healthcare more affordable. However, coverage can vary by state, and there may be limits on eligible providers and types of treatments.
Components of a Health Insurance Policy

Policy Premiums
Your premium is the “ticket price” of your insurance policy. Several factors influence it, including your age, health status, lifestyle habits (like smoking), and the amount of coverage you choose. Younger, healthier people usually pay lower premiums, while older individuals or those with health risks pay more.
Premiums can be paid monthly, quarterly, or annually. Some insurers also offer discounts for longer commitments, like paying two or three years in advance. While it might seem tempting to choose the cheapest premium available, remember that low premiums often mean reduced coverage.
Deductibles and Copayments
Deductibles and copayments are two of the most misunderstood elements of a health insurance policy, yet they directly affect how much you pay out-of-pocket.
A deductible is the amount you must pay before your insurer starts covering costs. For example, if your deductible is $1,000, you’ll need to spend that amount first on covered healthcare services before your insurance kicks in. Higher deductibles usually mean lower premiums, which is great for people who don’t expect to use their insurance often. On the flip side, if you have frequent medical needs, a lower deductible might save you money in the long run.
A copayment (or copay) is different. This is a fixed amount you pay for specific services, regardless of the total bill. For instance, you might pay $30 for a doctor’s visit or $15 for a prescription drug. Copays make healthcare costs more predictable, but they can add up over time, especially if you need regular medical attention.
Coverage Limits and Exclusions
Every health insurance policy has its boundaries. While the term “coverage” sounds comprehensive, it’s not a blanket guarantee for every medical expense. Policies come with coverage limits and exclusions that every policyholder must be aware of.
-
Coverage Limits: These may be overall (like $100,000 per year), or specific to conditions (like $10,000 for maternity expenses). Some policies also have sub-limits for room rent in hospitals, ambulance charges, or specific surgeries.
-
Exclusions: These are treatments your policy will never cover. Common exclusions include cosmetic surgery, fertility treatments, dental work (unless accidental), and self-inflicted injuries. Many policies also exclude pre-existing conditions for a waiting period, typically ranging from 1 to 4 years.
Network Hospitals and Cashless Claims
One of the biggest perks of health insurance today is cashless treatment. This means you don’t have to pay out-of-pocket during hospitalization; your insurer directly settles the bill with the hospital. But here’s the catch: this facility is available only at network hospitals tied up with your insurer.
When buying a policy, always check the list of network hospitals. The more extensive the network, the more flexibility you have in choosing where to receive treatment. Some insurers also offer tie-ups with premium hospitals, which adds extra value.
How Claims Work in Health Insurance

Cashless Claims Process
Cashless claims make hospitalization much smoother. Here’s how it typically works:
-
You visit a network hospital and show your health insurance card.
-
The hospital contacts your insurer or Third Party Administrator (TPA) for approval.
-
Once approved, your treatment begins without you paying anything upfront (except non-medical expenses like food).
-
After treatment, the hospital sends the bill directly to your insurer for settlement.
Reimbursement Claims Process
If you get treated at a non-network hospital, you’ll need to go through the reimbursement process. It works like this:
-
Pay your hospital bills at the time of discharge.
-
Collect all receipts, reports, and discharge summaries.
-
Submit these documents along with a claim form to your insurer.
-
The insurer reviews and verifies the documents.
-
Once approved, the insurer reimburses the eligible amount to your bank account.
Documents Required for Claim Settlement
When filing a claim, you’ll need to provide certain documents. Commonly required ones include:
-
Completed claim form
-
Health insurance card copy
-
Hospital bills and receipts
-
Diagnostic reports and prescriptions
-
Discharge summary
-
ID proof (Aadhar, passport, etc.)
Common Reasons for Claim Rejection
Unfortunately, not all claims get approved. Understanding why claims are rejected can help you avoid costly mistakes. Common reasons include:
-
Treatment is not covered under the policy
-
Pre-existing condition within the waiting period
-
Submitting incomplete or false documents
-
Exceeding policy limits or sub-limits
-
Delay in claim submission
Benefits of Having Health Insurance
![]()
Financial Protection During Medical Emergencies
The biggest advantage of health insurance is financial security. Imagine needing a surgery costing $15,000 without insurance; that’s money straight out of your pocket. With insurance, your out-of-pocket expense could drop to a few hundred dollars, depending on your policy.
Health insurance essentially acts as a financial cushion, protecting your savings from being wiped out by unexpected medical bills. This is especially critical in countries where healthcare costs are rising at double-digit rates every year.
Access to Quality Healthcare
Having insurance often means better and quicker access to top-tier hospitals and specialists. Many premium hospitals prefer insured patients since payments are guaranteed through insurers. Without insurance, you might find yourself restricted to lower-cost facilities or struggling to arrange funds before treatment.
Tax Benefits of Health Insurance
In many countries, buying health insurance isn’t just about protection; it also saves you money on taxes. For example, in India, under Section 80D of the Income Tax Act, premiums paid for health insurance can be deducted from taxable income, reducing your overall tax burden.
In the U.S., health insurance purchased through the Affordable Care Act marketplace may qualify you for subsidies and tax credits, depending on your income level. These benefits make insurance not just a health decision but a smart financial one too.
Peace of Mind for Families
At the end of the day, health insurance is about peace of mind. Knowing that you and your loved ones are protected from massive medical expenses reduces stress significantly. Emergencies are unpredictable, but insurance ensures that money doesn’t come in the way of getting the right treatment.
Families with children or elderly parents particularly benefit from comprehensive coverage, as medical care for these age groups is often frequent and costly. Insurance ensures that your family’s well-being is never compromised due to financial constraints.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Health Insurance Policy
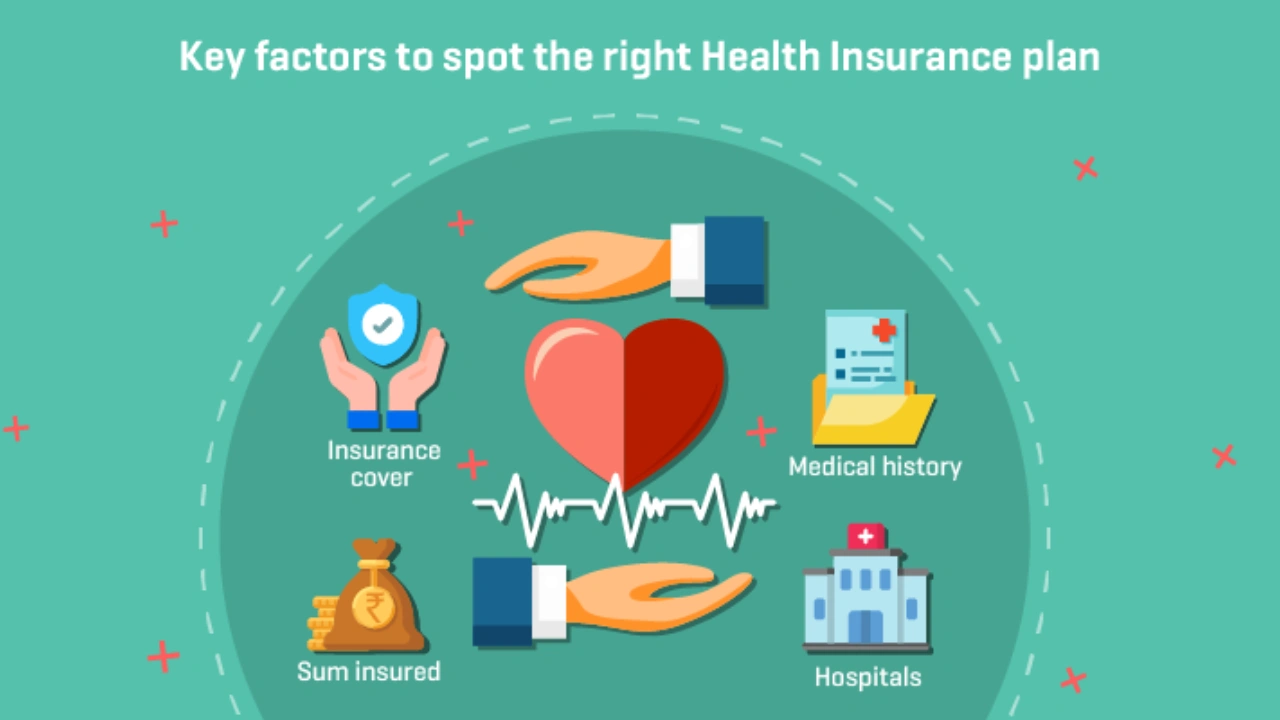
Coverage Amount and Sum Insured
One of the first things you should consider when choosing a health insurance policy is the sum insured, which is essentially the maximum amount the insurer will pay in case of medical treatment. Choosing the right coverage amount depends on factors like your age, lifestyle, family size, and healthcare costs in your city.
For instance, if you live in a metropolitan city where hospitalization costs are higher, a coverage amount of at least $100,000 might be necessary for adequate protection. On the other hand, if you live in a smaller town with relatively lower medical costs, a smaller coverage may suffice.
A common mistake people make is opting for a low coverage amount to save on premiums. But in reality, underinsuring yourself could be financially devastating. Imagine having a policy worth $20,000 when your hospital bill is $40,000; you’ll still have to pay the remaining $20,000 out-of-pocket. Therefore, it’s always better to choose a higher sum insured, even if it means slightly higher premiums.
Network Hospitals and Services
The network hospital list is another crucial factor. Insurance companies tie up with certain hospitals to provide cashless treatments. If your preferred hospital isn’t on the list, you might have to pay upfront and claim reimbursement later, which can be inconvenient during emergencies.
When selecting a policy, check whether the insurer has tie-ups with reputable hospitals near your home or workplace. The wider the hospital network, the more flexibility you have in emergencies. Some insurers also provide access to specialized facilities like private rooms, premium healthcare packages, and wellness programs in their network hospitals, which adds more value to your policy.
Pre-existing Diseases and Waiting Periods
Most insurers impose a waiting period for pre-existing diseases (PEDs), which can range from 12 months to 4 years. During this period, any treatment related to your existing condition (like diabetes, hypertension, or asthma) will not be covered.
If you have pre-existing health conditions, look for policies with shorter waiting periods or insurers that offer coverage for PEDs at higher premiums. Transparency is key here; always disclose your health history truthfully when buying a policy. If you hide a condition and it gets discovered later, your claim may be rejected altogether.
Add-on Riders and Benefits
Health insurance policies can be customized using add-on riders. These riders offer additional benefits that can make your policy more comprehensive. Some popular add-ons include:
-
Critical Illness Rider: Provides a lump sum payout if you’re diagnosed with a major illness like cancer or stroke.
-
Maternity Cover: Covers expenses related to pregnancy and childbirth.
-
Personal Accident Cover: Provides financial compensation in case of accidental disability or death.
-
Room Rent Waiver: Removes restrictions on room rent charges during hospitalization.
Myths About Health Insurance

“I’m Young, I Don’t Need Health Insurance”
Many young people think they’re invincible and don’t need insurance. But the truth is, accidents and sudden illnesses can happen to anyone. Starting young actually works in your favor; you get lower premiums and longer coverage without exclusions. Plus, buying early ensures that waiting periods for pre-existing conditions are completed before you actually need coverage.
“Employer’s Health Insurance is Enough”
Relying solely on your employer’s group insurance is risky. The coverage amount is often limited, and once you leave the company, the insurance ends. Having a personal policy ensures continuous coverage, regardless of your employment status. It’s best to treat employer-provided insurance as a bonus, not your primary protection.
“Health Insurance Covers All Medical Costs”
This is one of the biggest misconceptions. Health insurance does not cover every single expense. Non-medical costs like consumables, personal items, or experimental treatments are usually excluded. Some policies also impose limits on room rent, ambulance charges, or specific procedures. Always read the fine print to understand what’s excluded.
“Cheaper Plans are Always Better”
Low-premium plans often come with restricted benefits, limited hospital networks, high deductibles, or exclusions. Choosing a plan solely based on price can leave you underinsured when you need it most. Instead, look for a balance between affordability and adequate coverage.
Challenges in Health Insurance

Rising Premium Costs
How Health Insurance Policies Work: One of the biggest challenges policyholders face today is the steady rise in premium costs. As healthcare costs soar globally, insurers adjust premiums accordingly. Age also plays a role in your premium increases as you get older. For families, especially with elderly parents, premiums can become significantly high.
A good strategy to combat this is to buy insurance early and opt for long-term policies with fixed premiums. Some insurers even offer a “no-claim bonus” (NCB), where your coverage increases if you don’t file claims in a year, giving you more value for money.
Complex Terms and Conditions
Let’s face it, insurance policies are filled with jargon. Words like deductible, coinsurance, or exclusions often confuse policyholders. This complexity discourages many from buying insurance or leads them to choose the wrong plan.
To overcome this, insurers are now simplifying documents and offering digital policy explainers. As a buyer, you should always ask your agent or read simplified guides before signing up. Never assume coverage without clarity; it could cost you later.
Fraudulent Claims and Rejections
Fraudulent claims are a big issue in the insurance industry. Some people misuse policies by submitting fake bills or inflated claims. To tackle this, insurers have strict verification processes, which sometimes lead to genuine claims being delayed or rejected.
The solution is simple: always submit authentic documents and maintain transparency. Keep copies of every medical report and bill. If your claim is unfairly rejected, you can escalate it to the insurance ombudsman or regulator for resolution.
Lack of Awareness Among Policyholders
Surprisingly, many people don’t fully understand their policies. They might not know about waiting periods, exclusions, or sub-limits until it’s too late. Lack of awareness is one of the biggest challenges in ensuring smooth claim settlements.
This is why reading your policy document, asking questions, and staying updated with policy changes are necessary. Many insurers now provide mobile apps where you can track your coverage, claims, and even chat with representatives for clarity.
Future of Health Insurance

Role of Technology in Health Insurance
How Health Insurance Policies Work: Technology is transforming health insurance at lightning speed. From mobile apps to AI-powered tools, insurers are now leveraging digital innovations to make policies more accessible, transparent, and user-friendly. Customers can now buy, renew, or claim policies online without lengthy paperwork.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are being used to analyze customer data and predict health risks. This helps insurers design customized policies instead of offering one-size-fits-all coverage. Blockchain technology is also being explored to make claim settlements faster and more secure by reducing fraud and paperwork.
For policyholders, this means more convenience, faster processing, and policies tailored to their lifestyle and health habits. Instead of waiting weeks for claim approval, many digital-first insurers now settle claims within hours using automated systems.
Telemedicine and Digital Health Coverage
Telemedicine consulting doctors online via video calls has become a game-changer in healthcare. Health insurers are quickly adapting by including telemedicine consultations as part of their coverage. This is especially useful for routine check-ups, minor illnesses, or for patients living in rural areas with limited access to hospitals.
Digital health coverage also includes fitness tracking and wellness programs. Many insurers now partner with apps and wearable devices (like smartwatches) to encourage healthy lifestyles. Some even reward policyholders with discounts or cashback if they meet fitness goals. This not only promotes preventive care but also reduces overall medical costs in the long run.
Personalized and AI-based Insurance Plans
The future of insurance is personalized coverage. Instead of paying for benefits you don’t use, insurers are beginning to offer tailored plans based on your personal health profile. For example, a young professional may get a lower-cost plan with more accident coverage, while an elderly person may have a policy focused on chronic illnesses.
AI will play a crucial role here. Imagine an insurer monitoring your health via wearable devices and adjusting premiums or offering wellness incentives accordingly. This approach not only benefits insurers by reducing risks but also empowers customers to take control of their health.
Global Health Insurance Trends
Across the world, health insurance is evolving to meet the growing demand for affordable and accessible healthcare. Some key global trends include:
-
Universal Health Coverage (UHC): Many governments are working towards providing health insurance for all citizens.
-
Cross-Border Insurance: With increased global travel, insurers are offering plans that provide international coverage.
-
Mental Health Coverage: More policies now include counseling and psychiatric treatments, acknowledging the importance of mental health.
-
Value-Based Insurance: Instead of simply paying for treatment, insurers are focusing on preventive care and rewarding healthier lifestyles.
Conclusion
How Health Insurance Policies Work: Health insurance is no longer a luxury; it’s a necessity. Medical costs are rising, and one unexpected illness or accident could drain your savings in no time. By understanding how health insurance policies work, what terms like premiums and deductibles mean, and how claims are processed, you can make smarter decisions that protect both your health and finances.
Choosing the right policy is not just about the lowest premium; it’s about finding a balance between adequate coverage, trusted insurers, and long-term affordability. With the rise of digital tools and personalized coverage, the future of health insurance is brighter, more efficient, and more customer-friendly than ever before.
FAQ
What is the best age to buy health insurance?
How Health Insurance Policies Work: The best time to buy health insurance is in your 20s or early 30s. At this stage, premiums are lower, and you complete waiting periods for pre-existing diseases well before you might actually need coverage.
Can I have multiple health insurance policies?
How Health Insurance Policies Work: Yes, you can. If one policy doesn’t cover the full expense, you can claim the balance from another. However, you need to inform all insurers about existing policies to avoid claim disputes.
Does health insurance cover pre-existing conditions?
How Health Insurance Policies Work: Yes, but usually after a waiting period of 1 to 4 years. Some policies offer shorter waiting times or higher premiums for immediate coverage.
How is the health insurance premium calculated?
How Health Insurance Policies Work: Premiums are based on factors like age, health condition, coverage amount, lifestyle habits, and type of plan. Younger, healthier people usually pay less compared to older individuals.
What should I do if my health insurance claim is rejected?
How Health Insurance Policies Work: First, check the rejection reason. If it’s due to missing documents, resubmit with the required details. If you believe the rejection is unfair, escalate it to your insurer’s grievance cell or the insurance ombudsman.






